|
Last month, our tip described how AERMET reads custom meteorological data via its Onsite Pathway. AERMET’s Onsite Pathway gives users full control over how the model will read the data provided by the modeler, but there are some general conventions that must still be followed. Let’s take a closer look at some of the rules and guidelines for how the Onsite data file should be written.
Identifying Variables
AERMET can read over 20 unique meteorological variables from single surface-level measurements – such as pressure, radiation, or precipitation amount – to variables recorded at multiple heights or levels above ground (see below for more info on multi-level variables).
- Convention: While not explicitly required, AERMET generally prefers for single-level variables be listed prior to multi-level variables.
- Convention: The same variables must appear for all observation periods.
- Note: Not all variables are currently read by AERMET. Table B-4 of the US EPA’s AERMET User Guide identifies which variables can be left out.
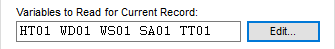
In AERMET View, use the Edit button to open the Onsite Variables dialog and identify which variables are in your file.
Multiple Levels
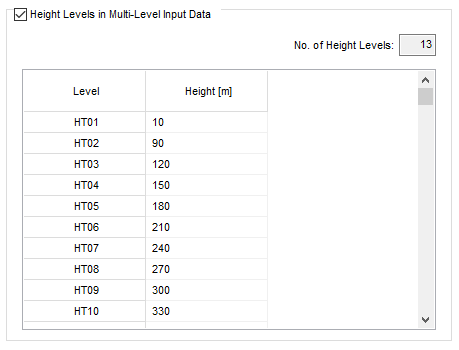
Variables such as wind and temperature can be recorded from multiple heights above ground. AERMET allows modelers to input data from as many as 50 different measurement heights. This data is written to the Profile met file (*.PFL) created by AERMET and allows AERMOD to generate an accurate vertical profile of the atmosphere when modeling. For example, AERMOD will use the wind data measured closest to stack height for each source.
Multi-level variables are identified using an integer to specify which height the variable is observing starting closest to the ground. For example, TT01 refers to temperature data (TT) from the level nearest to ground (01) while WS02 identifies wind speed (WS) from the next lowest level (02).
In AERMET View, height values can either be identified as a variable in the data string (use the HTnn variable) or via the Additional Parameters tab.
Height Levels in AERMET View
Sub-Hourly Observations
While AERMET’s Surface Pathway only identifies hourly observations, the Onsite Pathway can read up to 12 periods in a single hour (5-minute resolution). AERMET then calculates an hourly average for each parameter and processes the hourly data.
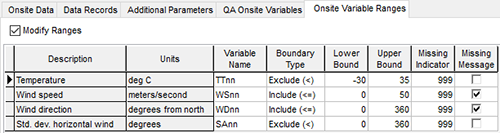
- Convention: Time steps must be even and consistent, so do not leave gaps if you have missing data. Instead, input the sequential time stamp (year, month, day, hour, minute) and use a Missing Indicator to flag any missing data.
In AERMET View, the Missing Indicator for each variable can be customized via the Onsite Variable Ranges tab.
With the above information and the tools available in AERMET View, users can efficiently process their custom meteorological data for use in the AERMOD model.
|