The CALPUFF air dispersion modeling system is extremely powerful and contains many refined features for users to conduct air modeling. A consequence of the model’s refined nature means some calculations can take a very long time to complete, however. Some situations may call for a modeler to conduct multiple model runs thus compounding the runtimes.
To more quickly assess cumulative impacts from multiple independent runs, the CALSUM utility can be used to create a set of combined output data. CALSUM can support the following output data types:
- CONC.DAT (concentration)
- DFLX.DAT (dry deposition fluxes)
- WFLX.DAT (wet deposition fluxes)
CALPUFF View includes the CALSUM Wizard which steps users through the process of running CALSUM. It is important to note that CALSUM can only be used if:
- The output files are of the same type (containing either concentrations, wet deposition fluxes, or dry deposition fluxes)
- The time periods contained in the files are identical
- The species are the same and listed in the same order within the CALPUFF setup
- The receptors (e.g., sampling, discrete, etc.) are the same, in terms of number, location, and order
Once that information has been verified, follow these steps to run the CALSUM Wizard:
- Begin by exporting the sources from each project whose output will be combined. Use the Export | Sources menu option to save the sources to an Excel spreadsheet.
- Create a new project to store the combined results. Since the parameters from each run must be the identical, select the Save Project As option to create a copy of the currently opened project.
- Select the Import | Sources menu option and import the Excel spreadsheets you exported in Step 1. Your new project will now contain all of the sources whose output will be combined in CALSUM.
- Select Tools | CALSUM Wizard. On the first step, provide an optional title for the run. The input, list, and output files will be automatically created, but you can change the names of any files as desired. Click Next > when ready.
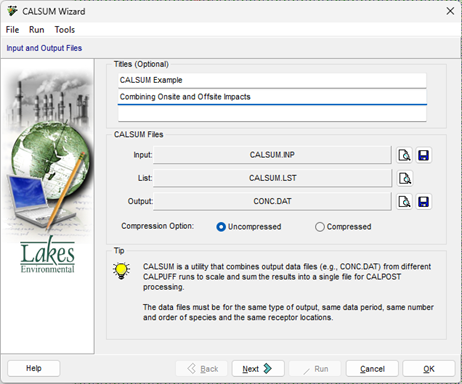
- Verify the Species list. Recall that the species must be the same and in the same order for all projects to be combined. You can import a Species List using the Import button (
 ). Click Next > to proceed.
). Click Next > to proceed.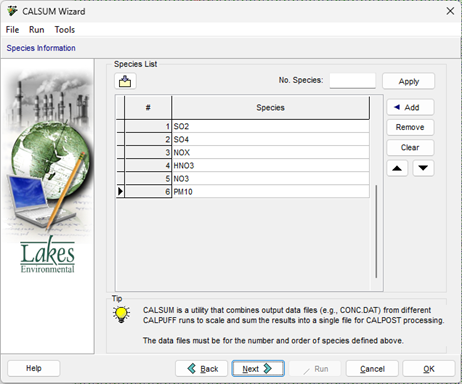
- Now specify in the Data Files and Scaling Options which output files will be combined. Select the Add File button to identify each unique output file.
The concentrations or deposition fluxes in each file may be scaled by using a linear operator of the form (A*x+B) where:
x represents either the concentration or deposition flux
A is the multiplicative constant (A-scale)
B is the additive constant
For example, you can use the B-Scale to add a constant background concentration to the model results. Enable the “Scaling Factor” checkbox for any specified output file to add scaling factors.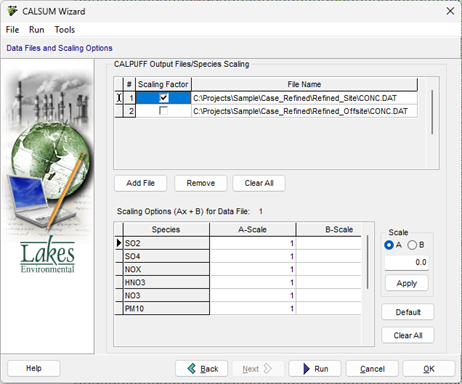
- After specifying all the CALSUM parameters, press the
 button to execute CALSUM. Click OK to close the CALSUM Wizard when the run is complete.
button to execute CALSUM. Click OK to close the CALSUM Wizard when the run is complete. - Re-run CALSUM as necessary to combine other output files (e.g., DFLX.DAT, WFLX.DAT).
- Once your output is combined, execute CALPOST for the newly combined files using CALPUFF View’s CALPOST Wizard.
- Verify your CALPOST model options. When the options are set, select Run | CALPOST Model to process the combined concentrations or deposition fluxes. The images below show Concentration results for a single source facility compared to cumulative concentration results prepared using CALSUM.
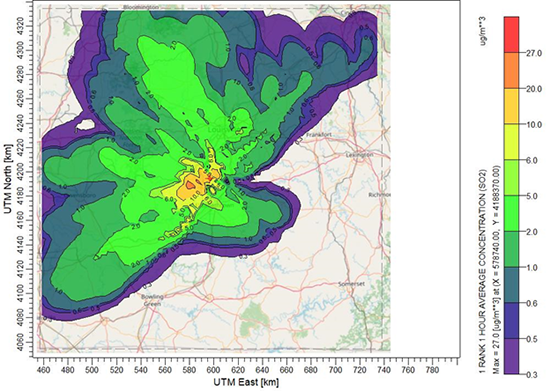
Sample 1-Hour SO2 Concentration Results from Single Source Facility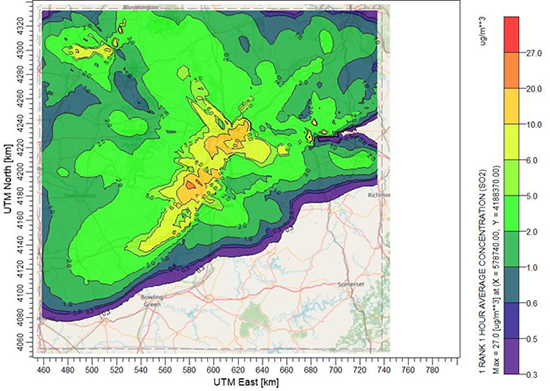
Sample 1-Hour SO2 Concentration Results from Cumulative Sources Prepared Using CALSUM