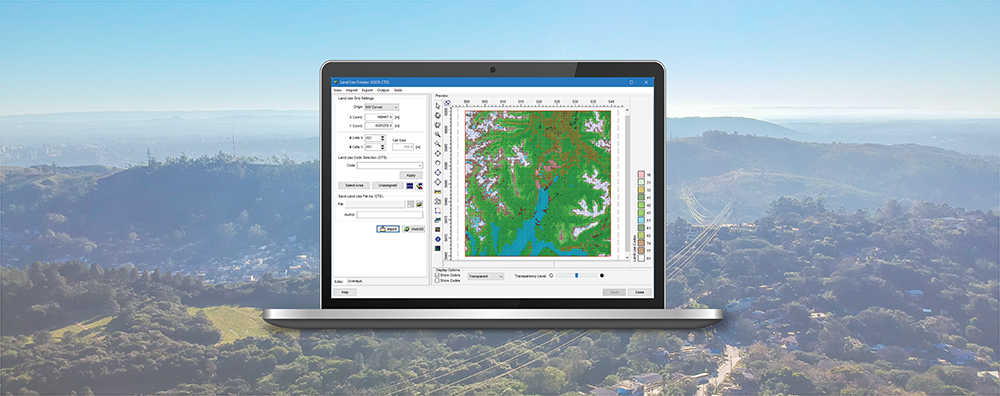
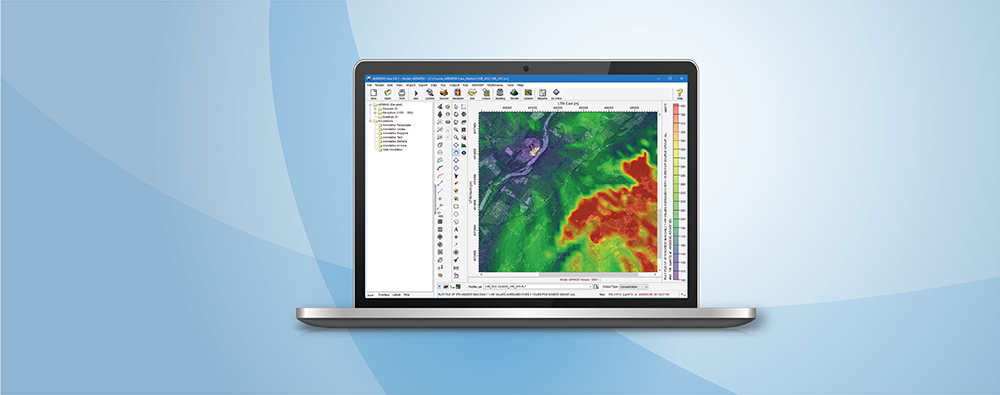
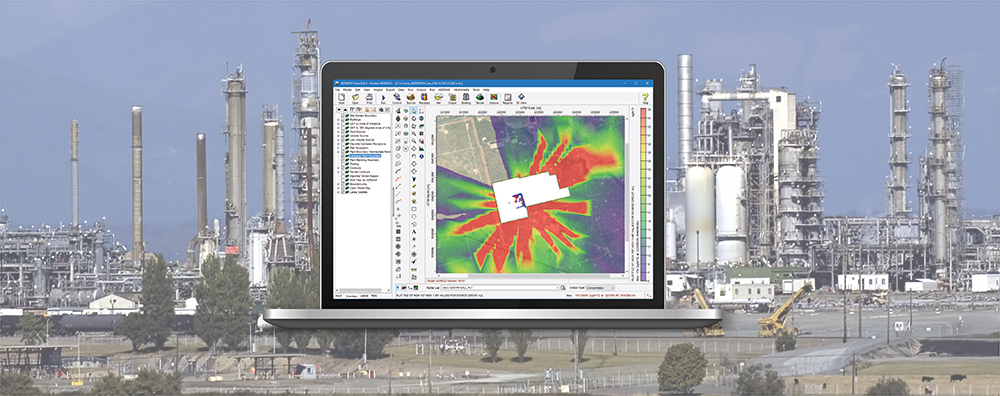
CALPUFF View: Mapping Land Use Data in Shapefile Format
Land use data is vital to air quality modeling because the types of land cover encountered within the modeling domain play a big role in calculating atmospheric stability. Turbulence parameterization will be very different in a heavily populated urban area compared to a flat, grassy field or a large body of water. Digital land use data is available in a wide variety of formats, and the new CALPUFF View Version 9.0 now allows users to import land use data in shapefile format.