Most users are aware of Lakes Environmental Software’s Import from Excel utility which reads hourly meteorological data from an Excel spreadsheet and generates a text-based data file in SAMSON format. The generated file can be used in a variety of air modeling applications.
The utility is featured in several of our products:
Step 1: In AERMET View and RAMMET View, it is found under the Tools | Hourly Surface Data | Import from Excel menu
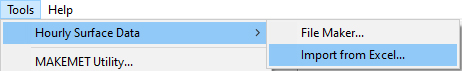
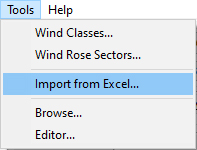
Step 2: In WRPLOT View, in the Tools | Import from Excel menu option
What some users may not realize is that there are two versions of the utility. Both versions work in the same way, but there is a fundamental difference between them: WRPLOT View is designed to import wind and precipitation data only.
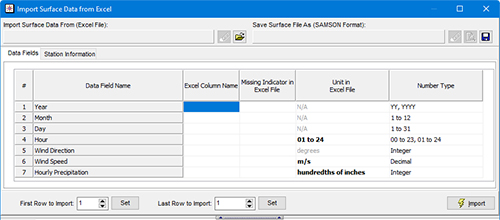
Import Surface Data from Excel in WRPLOT View
This way, users can quickly generate wind rose plots without worrying about unnecessary data variables.
In AERMET View and RAMMET View, the utility can read in all surface-level variables that would be required to run those preprocessors.
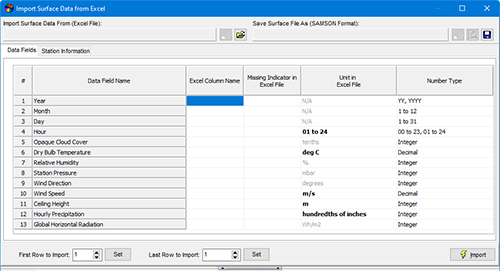
Import Surface Data from Excel in AERMET View
Here are some tips for using the utility:
To quickly set the Excel Column Name, right-click the columns in the Excel File tab and select from the variable list:
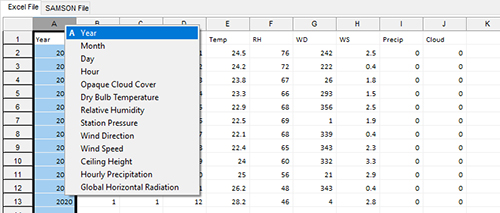
Not all variables are required. If your Excel sheet does not contain one of the listed parameters, just leave the Excel Column Name field blank and the utility will not attempt to read that data.
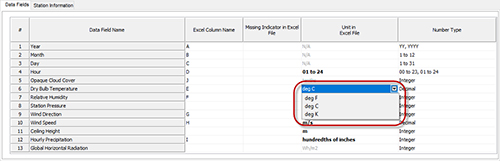
Pay attention to units. While some parameters – such as cloud cover, humidity, and wind direction – can only accept one unit, parameters like temperature, wind speed, and precipitation rate can accept different kinds of units.
The Station Information inputs are used to populate the header of the generated SAMSON file. Using the most accurate data possible will improve use of the file elsewhere – such as exporting to Google Earth or loading station information into AERMET View or RAMMET View.