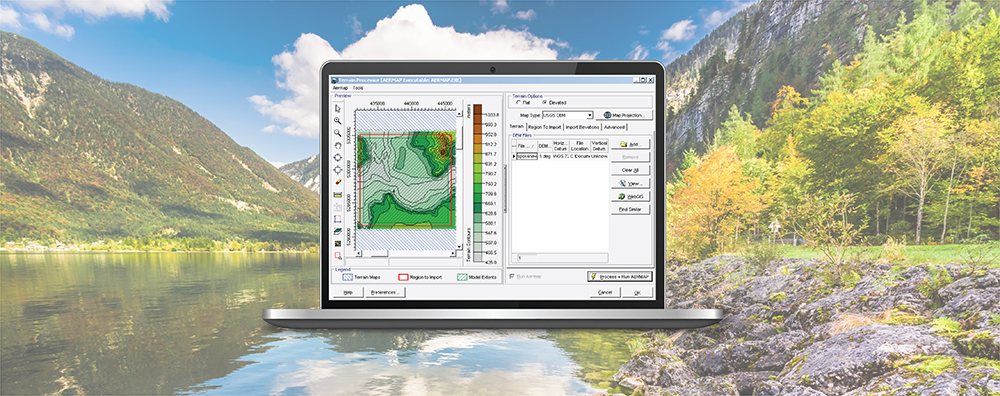
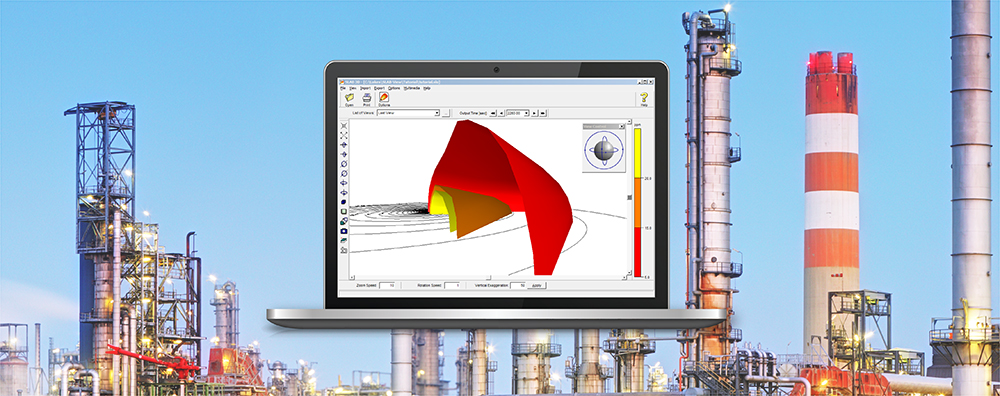
AERMOD View: Importing Gas & Particle Data
In addition to calculating air concentrations of pollutants, the AERMOD air dispersion model can calculate deposition fluxes from both particulate and gaseous emissions. When these routines are enabled, deposition parameters must be input to the model.