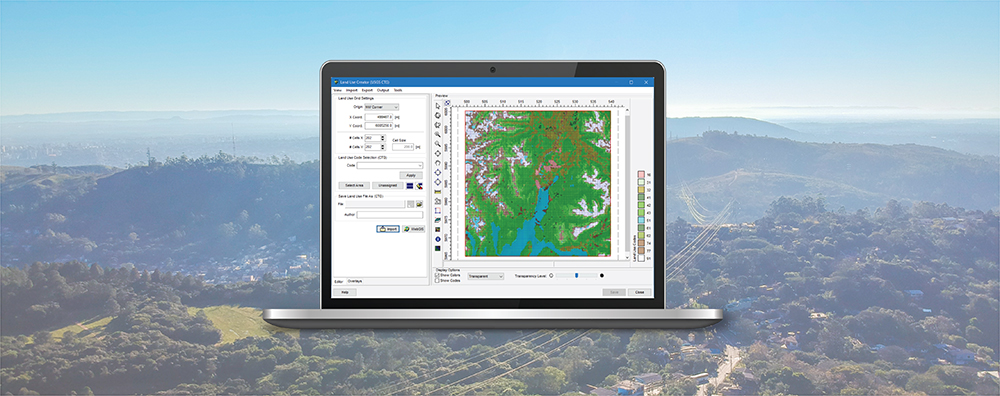
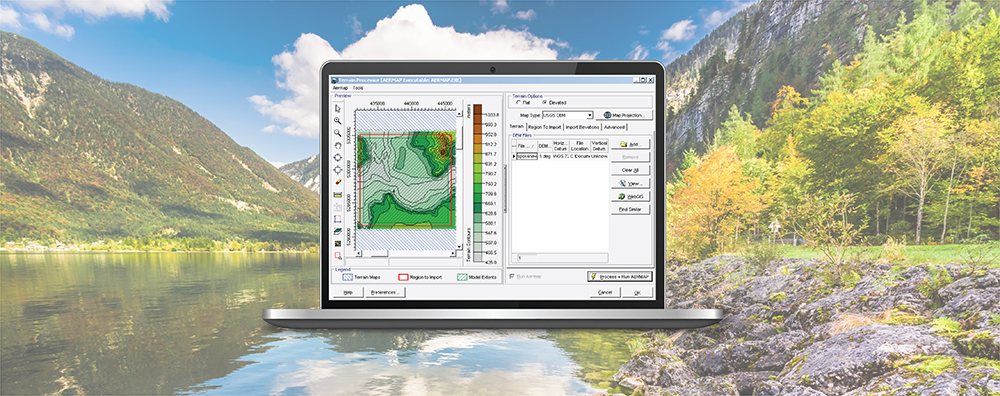
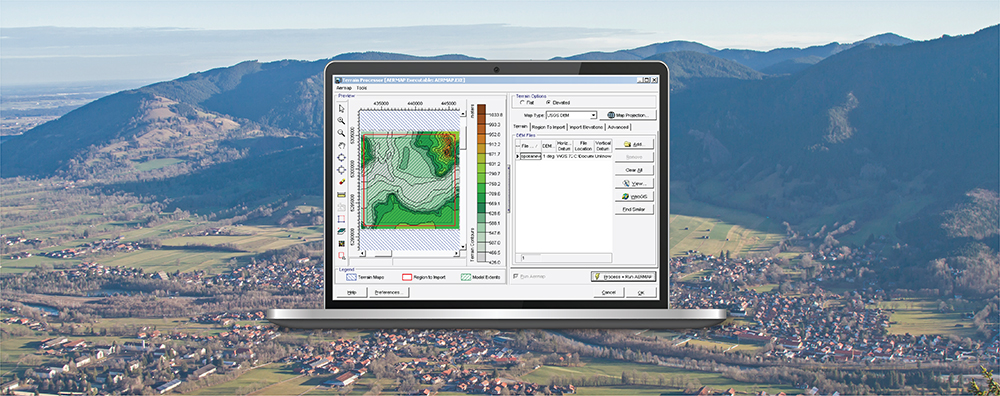
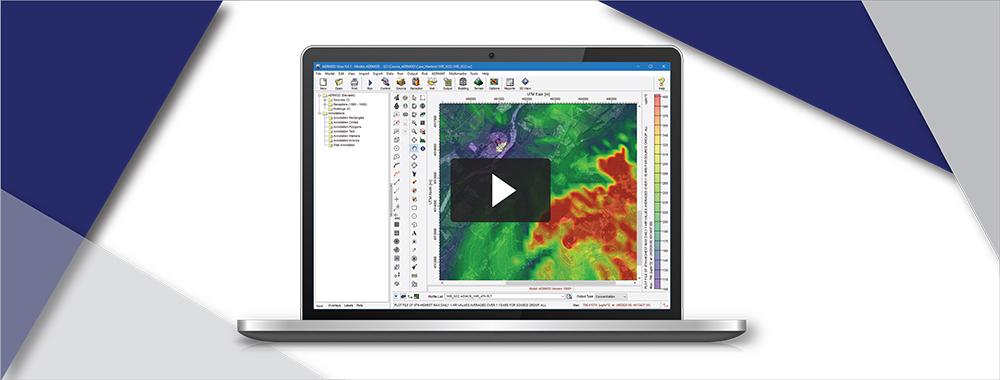
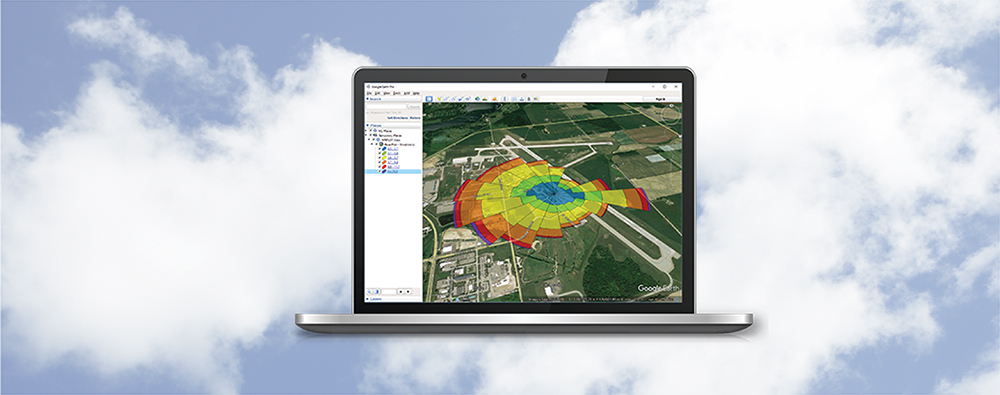
AERMOD View: Post-Processing Lead Concentrations in AERMOD with LEADPOST
In the United States, the National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS) for Lead is 0.15 µ/m3 as a rolling three-month average. This differs from other NAAQS in that it uses a rolling period, so a new three-month period is calculated with each successive month (e.g., January-March, February-April, etc.).