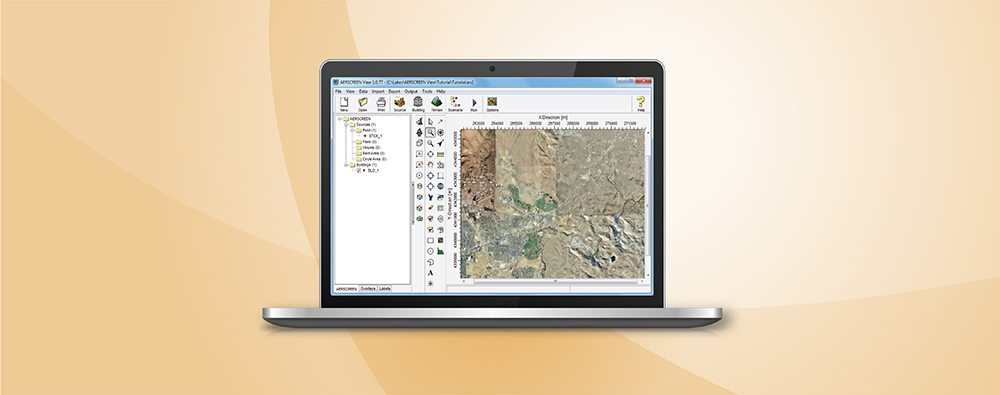
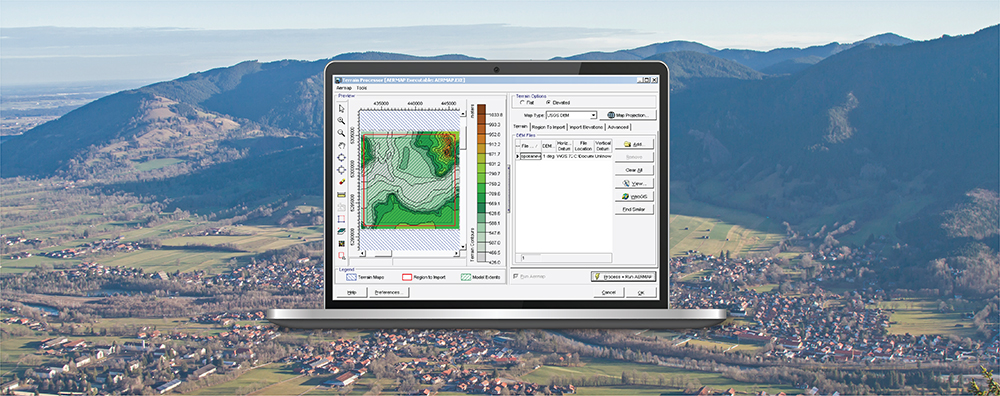
AERMOD View: Reporting Plant Boundary Results
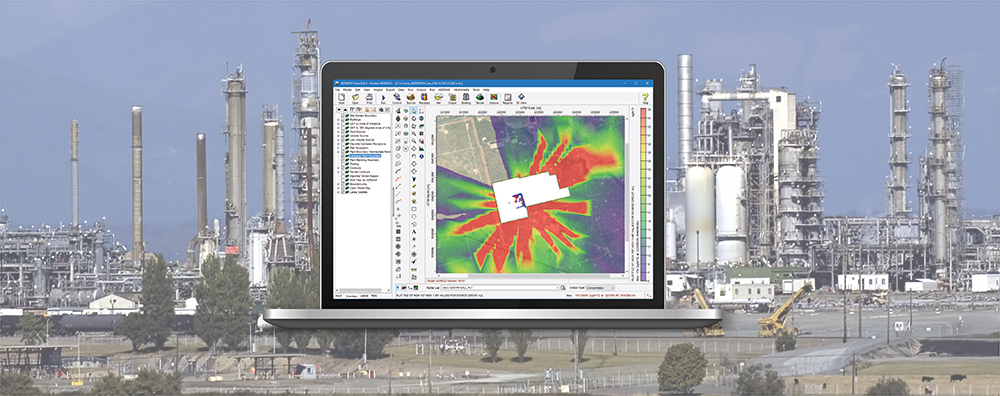
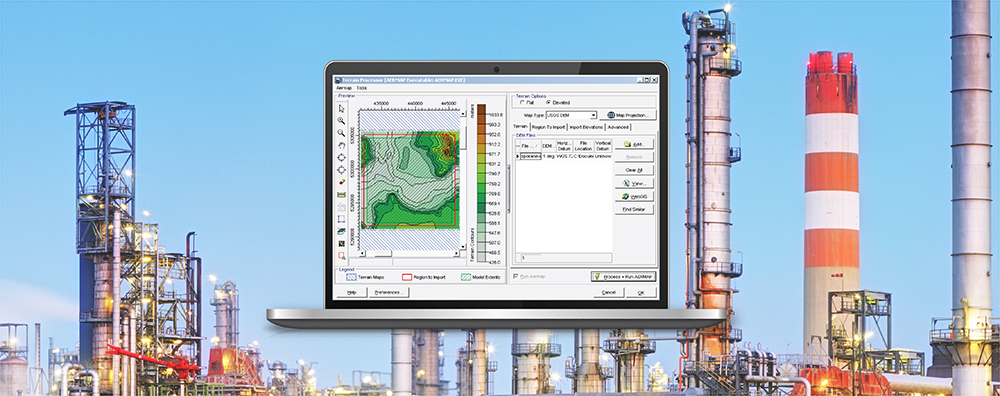
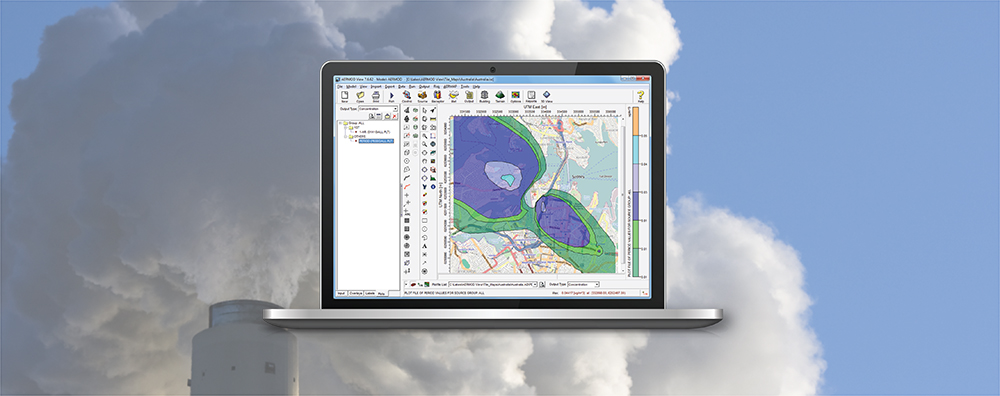
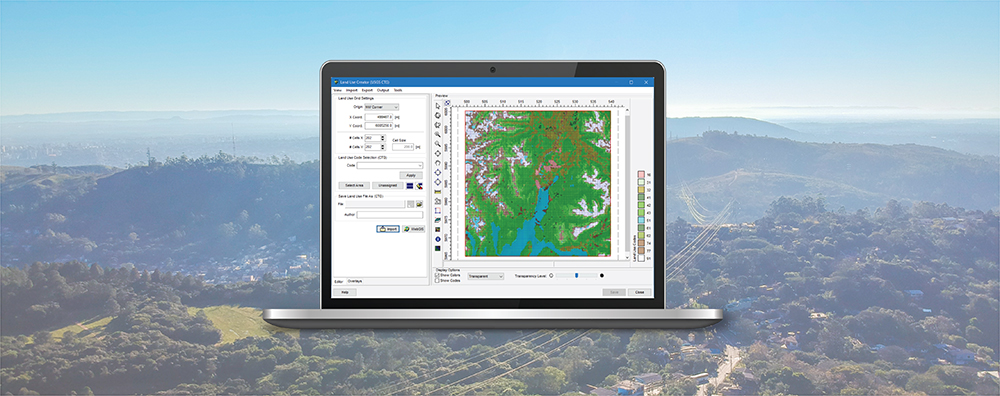
Previous Modeling Tips have covered different aspects of identifying plant boundaries in an AERMOD View project. This modeling tip describes plant boundary visualization capabilities and the ability to separate onsite and offsite impacts.