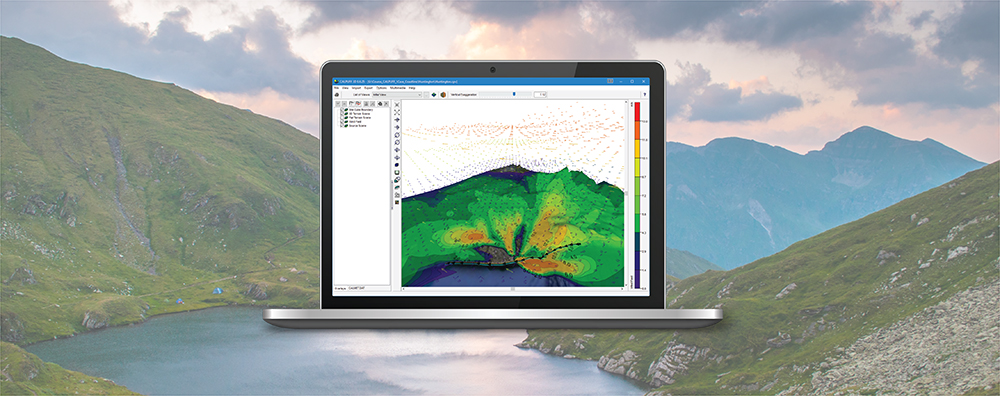
Lakes Software Applications: Graphical Options: Plot Colored Contour Lines
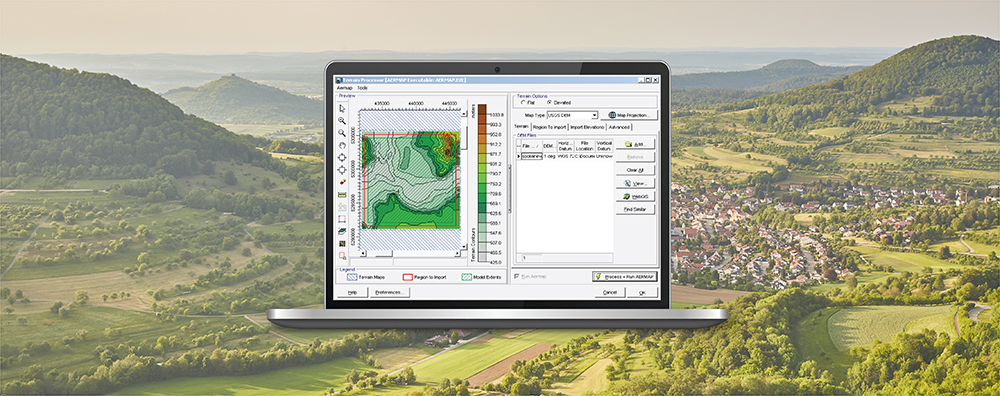
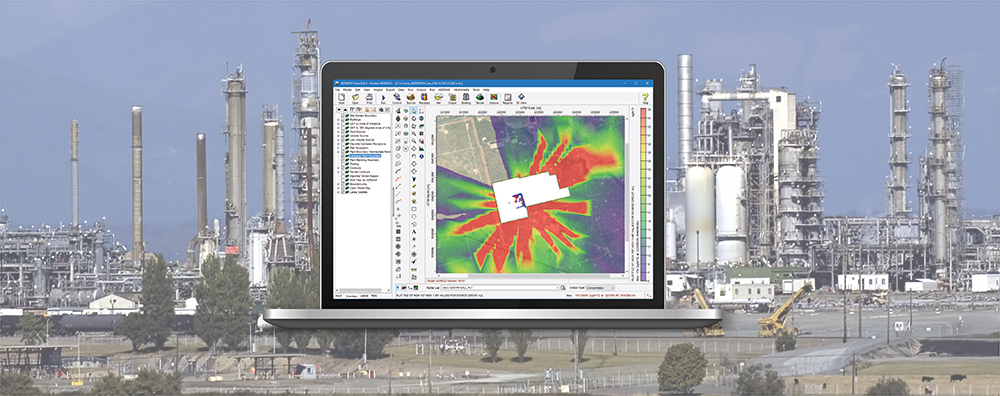
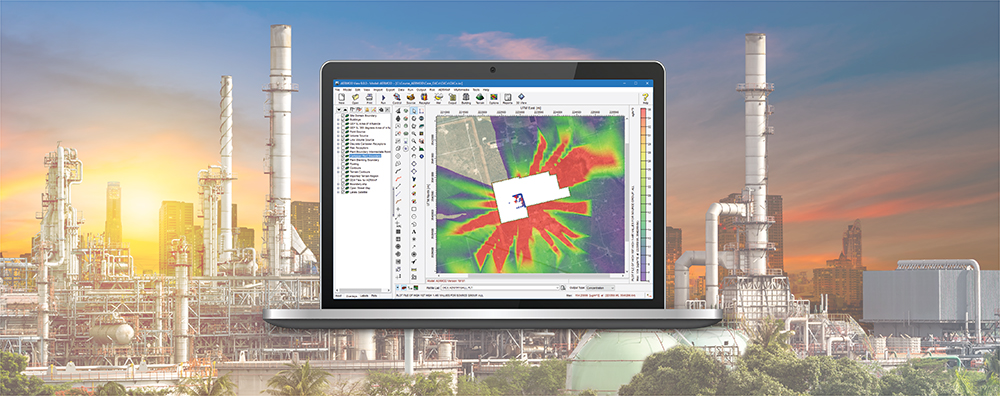
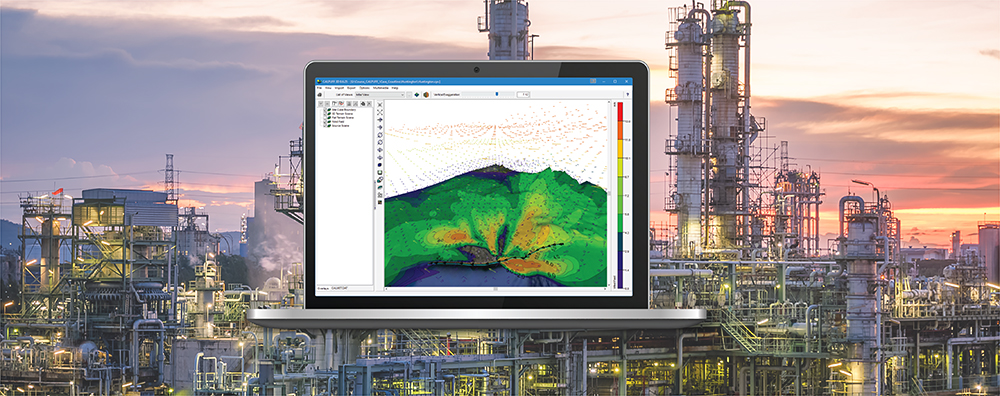
When conducting an air dispersion modeling analysis, the ability to present high-quality graphical depictions of the output is extremely important. Such images provide context to modeled results, and they provide a valuable tool to modelers in understanding and explaining the model’s calculations.