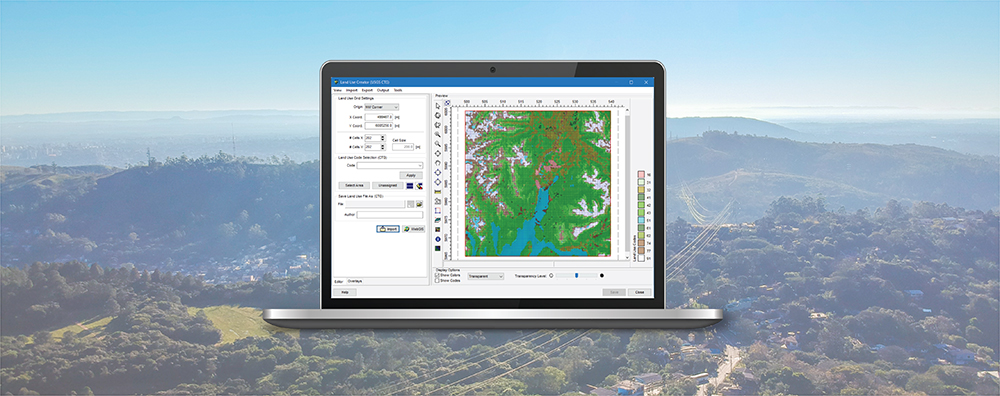
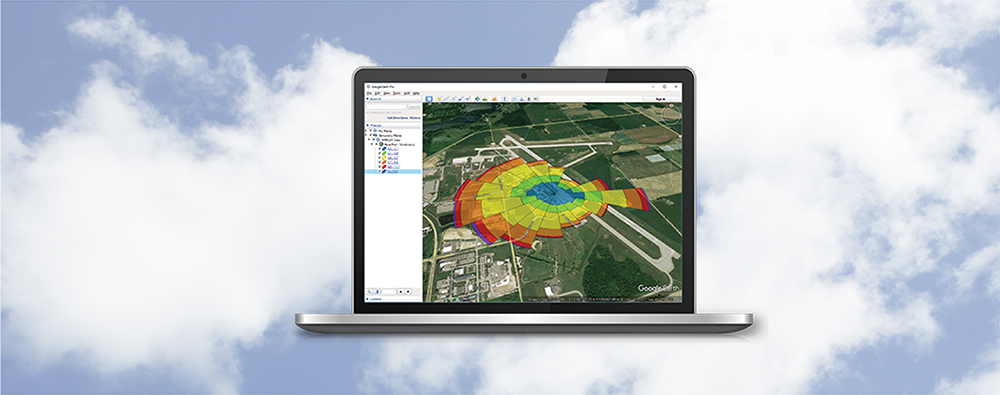
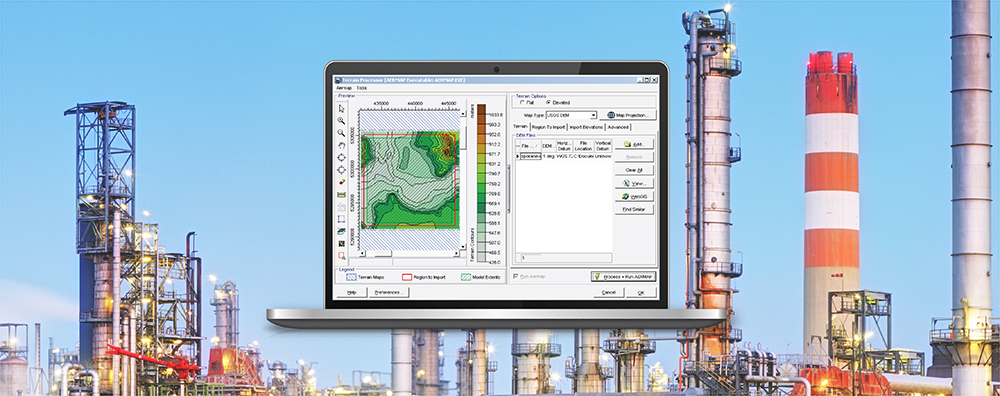
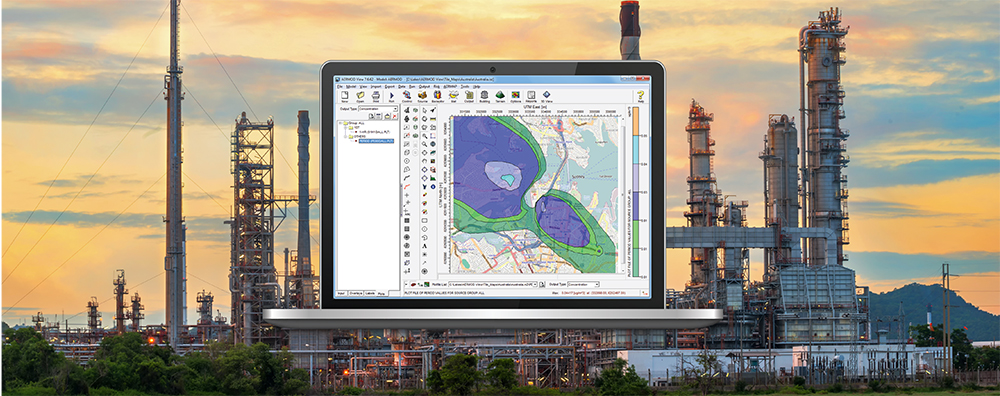
CALPUFF View: Changing the Default Text Editor
Most air dispersion models use simple text files for reading inputs and writing output data. To display these files, Lakes Environmental’s applications use the system’s default text editor. Users may prefer to use a different text editor to utilize different functionality or format data differently. To take advantage of these additional features, you can change the default text editor called by our software.