Previous Modeling Tips have looked at how to select pollutants in air quality models (AERMOD, CALPUFF). This month, we look at how to handle contaminants for a human health risk assessment project.
IRAP-h View, the Lakes-developed interface for conducting multi-pathway health risk assessment in accordance with the U.S. EPA OSW Human Health Risk Assessment Protocol (HHRAP), can analyze impacts from hundreds of unique compounds of potential concern (COPCs). Compounds include metals, organic compounds which survive the combustion process, and organic compounds which are formed immediately after combustion. There is no universal list of COPCs and should be selected based upon stack testing and facility-specific process information.
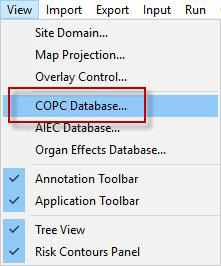
HHRAP includes Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS) numbers for over 200 individual compounds. These COPCs and their respective properties are available in IRAP-h View’s COPC Database accessible via the View menu or the Source Parameters | COPC Emissions settings.
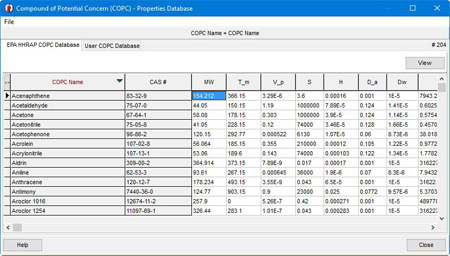
If non-listed COPCs are being analyzed, IRAP-h View allows for user-defined compounds to be added via the User COPC Database.
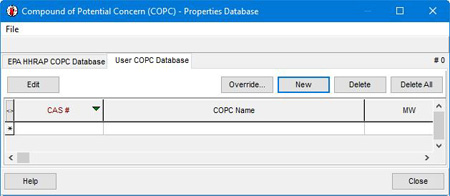
Select New to add a compound, then double-click the row to open the Chemical Parameters dialog. This allows you to quickly input all relevant properties, biotransfer factors, and health benchmarks.
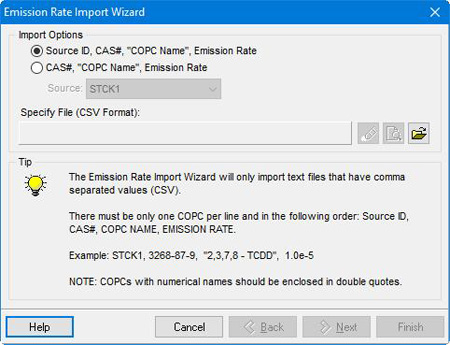
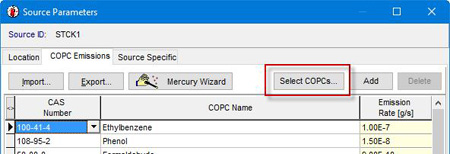
To add compounds to an IRAP-h View project, go the Source Parameters | COPC Emissions tab. COPCs are selected directly from the Database, and the emissions input in grams per second. COPCs and emissions can also be defined in CSV format and imported using the Emission Rate Import Wizard.