CALPUFF View: Automated Coastline Download
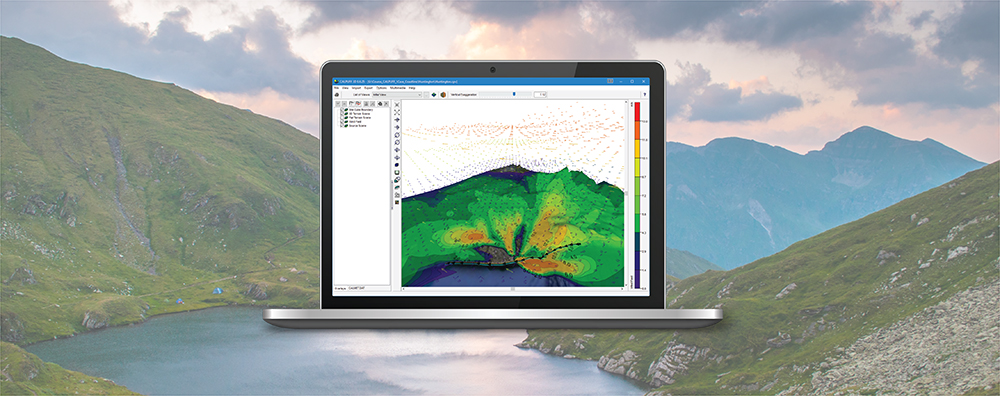
One feature of the CALPUFF model is the ability to depict coastal interaction effects. Since the land surface can heat more rapidly than adjoining water, a Thermal Internal Boundary Layer (TIBL) can form and bring elevated source plumes close to the ground.